We all have witnessed the sparks that are produced during the welding process. Even if you stand at quite a far distance from the welding place, yet your eyes would feel t
hat dazzling sensation which is very disturbing.I myself cannot look at those sparks as my eyes start to burn and I see blue spots all around. LOL!
Welders wear special glass goggles while working in order to protect their eyes from the harmful UV and IR radiations that are produced during the welding process. The UV rays have frequency ranging from 400nm to 0.6nm which are very harmful for the eyes and cannot be seen by the naked eyes. The glass windows in the special glass goggles for welders also prevent the dust, debris, fumes, welding spatters, and flying spark chips from entering the eyes.
In this article I am going to explain the components of special glass goggles for welding and tell you the significance of each part. Also, I will tell you what happens if you don’t wear those glasses during the welding process and what is the difference between safety glasses and welding glasses.
So, without further ado, let’s begin…
What dangers are posed to the eyes during the welding process?
Welding-related eye injuries come in various forms, like in the following circumstances stated below:
-
-
- Flying particles and chipped slag might cause mechanical damage by striking in the eyes
- It might cause photochemical and radiation burns from UV radiation, infrared radiation and intense blue light that are produced during the welding process
- Fumes and chemicals might cause chemical burns to the eyes and irritation in the eyes
-
What happens if you don’t wear?
If you do not wear special glass goggles that are especially designed for welding, it might cause fatal injuries to the eyes.
But before knowing about the injuries, let’s first know about the various types of welding:
-
-
- Gas metal-arc welding
- Shielded metal-arc welding
- Oxyacetylene welding
-
All these types of welding produce harmful ultraviolet, visible spectrum and infrared radiations. Amongst them, the damage from the UV rays occur the fastest. UV radiation gets absorbed in the cornea and the lens of our eyes and causes arc eye or arc flash that are very painful and often leave a permanent damage to the eyes. In least cases, it causes swelling of the eyes, redness, irritation, tearing and constant pain in the eyes.
One common condition that might result from not wearing the safety glass goggles is photokeratitis which is commonly known as snow blindness or arc eye which is a condition like having a sunburned eye. It directly affects the cornea and the conjunctiva. Though it is temporary but symptoms vary with the degree and the duration of the exposure to the welding light:
-
-
- Sensitivity to bright light
- Seeing halos
- Blurred vision
- Pain and irritation in the eyes
- Grittiness
- Constant teary eyes
- Swelling and redness of the eyes
- Feeling of sand particles being stuck in the eyes
-
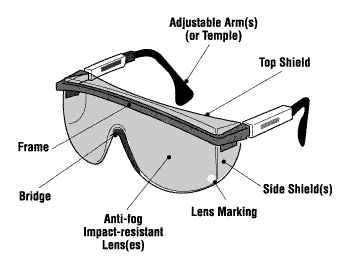
What are the different parts of welding goggles?
Eye protection in the welding industry is the most crucial, therefore; welding goggles are very carefully designed with each of these parts which have a significance of their own:
1.) Front frame: This is the part that holds and supports the lens.
2.) The rim or eyewire: This is the space where the glasses are attached.
3.) Bridge: This part connects the left and the right reams.
4.) Bar: This is the part of the bridge that is located above.
5.) End piece: Here the hinge of the glasses is located.
6.) Nose pad: This is the buffer frame that attaches to your nose.
7.) Guard arm: This is the supporting leg wherein the nose pad is attached.
8.) Paste/leg glasses: This is used to link the glasses with the ears of the wearer.
9.) Hinge: It connects the front frame and the temple or glasses leg.
10.) But portion: This is the place where the temple is located very close to the hinges.
11.) Bend: Here the protective goggles are curved downwards.
12.) The shaft: This is the part of the temple that connects the bend and the but portion.
13.) Earpiece or the temple tip: This is the tip of the temple.
14.) Dowel hole: This is the hinge hole that connects the temple and the rim.
15.) Side shields: This portion is used to cover the sides of the eyes in order to prevent sparks, dirt, debris fumes etc from entering the eyes.
16.) The straps: This is the rubber band that is used to hold the goggles to the face.
17.) The lenses: Lenses come in different shades and numbers for various welding activities which I am going to detail below!
Choosing the Perfect Glass Goggles for Welding
Choosing the wrong goggles can create several distractions and problems for you while working like the glasses getting fogged up with fumes, the color of the lens being too light for soothing the eyes, not having a side shield to prevent the debris and wedding spatters from entering the eyes.
Therefore, it is very important to choose the right goggles for welding in order to ensure safety and ease of work:
-
-
- The goggles should be vented in order to prevent fogging of the lenses.
- If dust, mists, fumes and gases are present around, it is better to choose the chemical goggles.
- Choose the ones with filtered plates that keeps out harmful radiations.
- Choosing the correct filter shade of the lenses is very essential. You should first start with choosing the shade that is too dark to see the welding zone and then go for the one that gives a sufficient view of the welding zone.
- The glass goggles should offer a snug fit. It should sit right at the bridge of the nose and the shielded area should be able to cover the sides of the eyes accurately. The straps too should offer a snug fit.
-
OSHA Guidelines for Safety Glass Goggles for Welding:
The US OSHA (1910.133(a)(5)) requires that:
“The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses equipment with filter lenses that have a shade number appropriate for the work being performed for protection from injurious light radiation.”
It also states that, “shielded metal arc welding, gas metal arc welding, and flux-cored arc welding require filter lenses with a minimum protective shade of 7, the highest required minimum being 11. Carbon arc welding requires a minimum of shade 14. Gas welding requires a minimum shade of 4.
OSHA also recommends that when choosing lenses, you start with a shade that is too dark to see the weld zone and then go to a lighter shade that allows a sufficient view, while still meeting the minimum requirements.
Choosing the right color of the lenses for different welding activities:
Not all shades are meant for every job, for example:
-
-
- Clear shade is fine for indoor works where there is no dealing with electricity
- Gold, silver and blue protect from glares of UV radiations
- Amber colored lenses are used for low light works
-
Choosing the right lens shade numbers:
Welding glasses come in various shade numbers and each shade number is designed for a particular job. The shade number is actually the indicator of the darkness of the lenses that are used in different welding activities. The welding processes that produce brighter arc would require higher shade numbers and vice versa. Let’s now check out the shade numbers and their usages:
| Shade number | Type of welding |
| Shade 3 | Torch brazing and soldering |
| Shade 8-12 | SMAW/STICK welding |
| Shade 14 | Carbon arc welding |
| Shade 9-13 | Mostly used in all welding activities |
Storing and care of the welding goggles:
-
-
- Always wipe the goggles clean after work and once you come back home. This will keep the goggles free from dirt and scratches.
- Store the goggles in the cases provided for the same in a cool dark and dust free environment.
-
It’s time to bid Adieu!
Eye is the most precious part of our body and once damaged your entire world turn dark!
Therefore, never compromise on wearing the right welding goggles for your work!
That’s all for today guys. We will be right back with another exciting article. Till then…
Take care, stay safe and…
Have a great day ahead!